OBJECTIVE : Creation of Multiple Excel Sheets in a Single Excel File when the Source record exceeds more then 65K.
SUMMARY : An Excel file "MyExcel" should be dynamically created. This Excel File "MyExcel" should have multiple Excel Sheets like "MyExcel1", "MyExcel2", "MyExcel3" dynamically created in it depending on the count of records in the source table. The source records are transferred to the destination Excel sheets in set of 65K records. Every Excel sheet must contain a max of 65K records from the source.
Coding Information :
1 - Variable Creation :
a) ExcelFileName : Specifies the name of the Excel File
Default value = Excel65K
b) ExcelFilePath : Specifies the full path of the Excel File
Default value = L:\practice\ssis\ExcelSheets\testexcel\
c) RowStartCount : Specifies the Starting count of the
records to be transferred to the Excel
Destination
Default value = 0
d) RowEndCount : Specifies the End count of the records to
be transferred to the Excel Destination
Default value = 0
e) RowSource : Count of records in the source table
Default value = 0
f) RowLimit : Maximum count of records that need to be
transferred to a single Excel Sheet
Default value = 50000
g) ExcelDestSheetName : Specifies the name of the Excel sheet
to which the data from the source
will be transferred.
Default value = Excel65K0
Evaluate As expression = TRUE
* For every set of records (equivalent to RowLimit i.e, 50000), a new ExcelDestSheetName will be generated dynamically and will be used in the Excel Destination Data flow destination.
h) QueryDFTSource : Specifies the dynamic query that selects
the required set of records from the
table. Here the set contains 50000
records in every loop, which is then
transferred to a new Excel sheet.
Evaluate As expression = TRUE
Query : "SELECT Column1
FROM ExcelOutflow
WHERE (Column1 >=" + (DT_WSTR, 10) @[User::RowStartCount] + " and Column1 <" + (DT_WSTR, 10) (@[User::RowEndCount] + @[User::RowLimit]) + ")"
Example : SELECT Column1
FROM ExcelOutflow
WHERE (Column1 >=0 and Column1 <50000)
i) QueryExcelSheetCreation : Contains the query to create the excel sheets dynamically in the excel file.
Evaluate As Expression = TRUE.
Query : "CREATE TABLE `"+ @[User::ExcelFileName] + (DT_WSTR, 25) @[User::RowStartCount] + "` ( `Column1` Decimal(5,0) )"
Example = CREATE TABLE `Excel65K0`
( `Column1` Decimal(5,0) )
2- Connection Managers :
a) Excel connection Manager
:: @[User::ExcelFilePath] + @[User::ExcelFileName] + ".xls"
:: Set the "ExcelFilePath" property of the Excel
connection manager to above expression
b) DataBase Connection Manager
c) File Connection Manager
* The Excel file present in the ExcelFileName variable has to be physically present initially so that in the DFT the mapping between source columns can be done with the destination columns. Else the Excel Destination will give error during the creation of the package.
3- Components Description :
The below image shows the Control Flow of the SSIS package.
Coding Information :
1 - Variable Creation :
a) ExcelFileName : Specifies the name of the Excel File
Default value = Excel65K
b) ExcelFilePath : Specifies the full path of the Excel File
Default value = L:\practice\ssis\ExcelSheets\testexcel\
c) RowStartCount : Specifies the Starting count of the
records to be transferred to the Excel
Destination
Default value = 0
d) RowEndCount : Specifies the End count of the records to
be transferred to the Excel Destination
Default value = 0
e) RowSource : Count of records in the source table
Default value = 0
f) RowLimit : Maximum count of records that need to be
transferred to a single Excel Sheet
Default value = 50000
g) ExcelDestSheetName : Specifies the name of the Excel sheet
to which the data from the source
will be transferred.
Default value = Excel65K0
Evaluate As expression = TRUE
* For every set of records (equivalent to RowLimit i.e, 50000), a new ExcelDestSheetName will be generated dynamically and will be used in the Excel Destination Data flow destination.
h) QueryDFTSource : Specifies the dynamic query that selects
the required set of records from the
table. Here the set contains 50000
records in every loop, which is then
transferred to a new Excel sheet.
Evaluate As expression = TRUE
Query : "SELECT Column1
FROM ExcelOutflow
WHERE (Column1 >=" + (DT_WSTR, 10) @[User::RowStartCount] + " and Column1 <" + (DT_WSTR, 10) (@[User::RowEndCount] + @[User::RowLimit]) + ")"
Example : SELECT Column1
FROM ExcelOutflow
WHERE (Column1 >=0 and Column1 <50000)
i) QueryExcelSheetCreation : Contains the query to create the excel sheets dynamically in the excel file.
Evaluate As Expression = TRUE.
Query : "CREATE TABLE `"+ @[User::ExcelFileName] + (DT_WSTR, 25) @[User::RowStartCount] + "` ( `Column1` Decimal(5,0) )"
Example = CREATE TABLE `Excel65K0`
( `Column1` Decimal(5,0) )
2- Connection Managers :
a) Excel connection Manager
:: @[User::ExcelFilePath] + @[User::ExcelFileName] + ".xls"
:: Set the "ExcelFilePath" property of the Excel
connection manager to above expression
b) DataBase Connection Manager
c) File Connection Manager
* The Excel file present in the ExcelFileName variable has to be physically present initially so that in the DFT the mapping between source columns can be done with the destination columns. Else the Excel Destination will give error during the creation of the package.
3- Components Description :
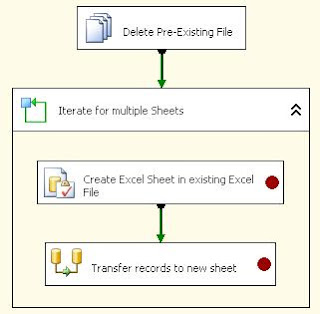
The below image shows the Control Flow of the SSIS package.
(Image-1)
File System Task "delete Pre-Existing Excel File" deletes the excel file with the same name if it is existing in the same location.
Execute SQL Task "Get Source Record Count" gets the count of records present in the source table.
For Loop Container "Loop for all records set..." loops for n number of times till all the records from the source table is transferred to the destination excel sheet.
(Image-2)
Here only the Evaluate Expression is specified.
The RowEndCount (default=0) is incremented with the value of RowLimit (default=50000) for every loop. So if the RowSource value is 200001, then the loop will continue for 5 times.
* The Assign Expression is specified in the Script Task present at the end of the For Loop.
(Image-3)
The Execute SQL Task "Create Excel Sheet in the Excel File" creates the excel sheets in the excel file.
The Connection Type should be EXCEL.
The excel sheet creation is done through a variable whose value changes dynamically with the For Loop execution.
* Refer above "Variables" part to know about its property.
(Image-4)
In the Data Flow Task "Transfer set of Records....." the OLEDB Source retrieves the data from SQL Server Table.
The command is passed to the source as a variable.
* Refer above "Variables" part to know about its property.
(Image-5)
In the Data Flow Task "Transfer set of Records....." the Excel Destination is configured with the variable "ExcelDestSheetName". The value of these variable changes for every loop of the For Loop Container.
It is very important to change the name since every new set of records need to be transferred to a new excel sheet which has been created dynamically in the Execute SQL Task.
* Refer above "Variables" part to know about its property.